 | Chapter 17. HyperSQL via ODBC |  |
| Chapter 16. HyperSQL on UNIX |  | Appendix A. Lists of Keywords |
Table of Contents
Support for ODBC access to HyperSQL servers was introduced in HSQLDB version 2.0. Improvements were made to the server code for version 2.5.1 to allow an unmodified PostgreSQL ODBC driver (version 11) to be used. This chapter has been adapted from the original ODBC documentation and added to this Guide.
The current version supports a large subset of ODBC calls. It supports all SQL statements, including prepared statements and result set metadata, but it does not yet support database metadata, so some applications may not work.
Install unixODBC and PostgreSQL psqlodbc RPM or package. See
https://help.interfaceware.com/v6/connect-to-postgresql-from-linux-or-mac-with-odbc
See the Settings section about individual driver runtime settings.
The unixODBC graphical program "ODBCConfig" just does not work for any driver I have ever tried to add. If the same applies to you, you will need to edit the files
/etc/unixODBC/odbc.ini Driver
definitions/etc/unixODBC/odbcinst.ini Global DSN
definitions$HOME/.odbc.ini Personal DSN
definitions Depending on your UNIX or unixODBC distribution, your
etc config files may be directly in /etc/ instead of
in the unixODBC subdirectory.
Download and install PostgreSQL ODBC software. We tested with version 11 of this software in Unicode mode, but other versions may also work. In Windows, go to ODBC Data Source Administrator (via Administrative Tools, Data Source (ODBC) or ODBC DataSource in different versions of Windows) and click on Add to add a PostgreSQL data source. You can then configure the data source.
See the Settings section about individual driver runtime settings.
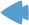
These DSN definition screens are not identical to what you see, but the individual settings are the same. The Data Source field is the name of the ODBC data source. The database is the name of the HyperSQL database on the server. In this example, the default server database name is indicated with a slash. Use localhost as the Server name for the local machine. The User Name is a user name of the HyperSQL database, by default SA. You must set a non-empty password for the user, otherwise connection cannot be established.
The HyperSQL server must be started before testing the connection.
 |
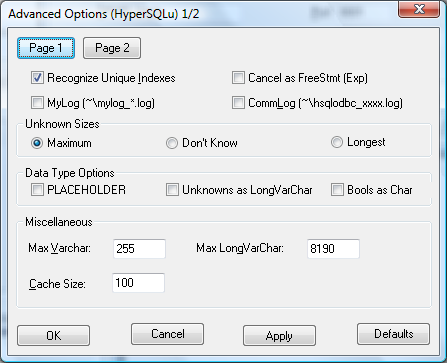
Then option screen 1 of 2.
 |
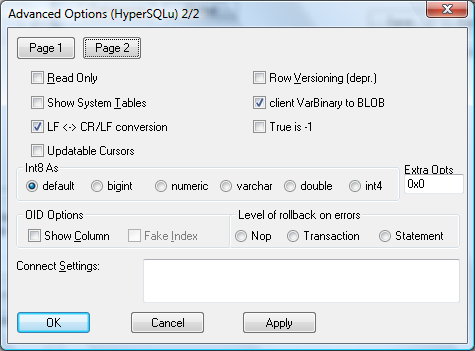
... and 2 of 2.
 |
This section applies to both UNIX and Windows. The setting heading includes the descriptive name as shown by the Windows ODBC DS Administrator, as well as the real keyword names that UNIX users will use.
The PostgreSQL ODBC Driver product consists of two driver
variants. You should try to use the Unicode variant
first, since it supports the later and better ODBC protocol. Use the
ANSI variant if the Unicode variant won't work for
your application. The way you select the driver variant for a DSN is
platform-specific. For UNIX, set the DSN setting Driver
to the key as defined in the uniXODBC config file
/etc/unixODBC/odbcinst.ini. For UNIX, select the
driver after you click Add on the User
DSN screen, or switch it afterwards with the DSN's
Manage DSN button.
Driver settings can also be made at connection time by just appending keyword abbreviation/value assignment pairs to the ODBC connection string, delimiting each such pair with a semicolon. Base connection Strings are language-dependent, but you always append a String in this form
;A0=0;B9=1
See the Table below for a concise list of the abbreviations you may use. The appendix also shows the default values for settings (this is really only necessary for UNIX users, since the Windows DSN manager always shows the current effective value).
Runtime Driver Settings
|
Database | ODBC does not allow an empty string for a DSN database name. Therefore, you must specify DSN database name of "/" (without the quotes) to indicate the default database |
|
Recognize Unique Indexes | |
|
Cancel as FreeStmt | Find out what this experimental feature is for. |
|
MyLog | Enables fairly verbose runtime logging to the indicated file. With value 1 will write coded mylog() messages to the MyLog file. With value 2 will write both mylog() and inolog() messages to MyLog file. |
|
CommLog | Enables runtime communiction logging to the indicated file. With value 1, will write coded qlog() messages to the CommLog. |
|
Unknown Sizes |
This controls what SQLDescribeCol and SQLColAttributes will
return as to precision for the variable data
types when the precision (for example for a column) is unspecified.
For the recommended
MS Access: Seems to handle Maximum setting OK, as well as all the others. Borland: If sizes are large and lots of columns, Borland may crash badly (it doesn't seem to handle memory allocation well) if using Maximum size. |
|
Max Varchar |
Use this setting only as a work-around for client app idiocy. Generally, the database should enforce your data constraints. The maximum precision of the VARCHAR and CHAR types (perhaps others). Set to 1 larger than the value you need, to allow for null terminator characters. The default is 255 right now. 0 really means max of 0, and we need to change this ASAP so that 0 will mean unlimited. If you set this value higher than 254, Access will not let you index on varchar columns! |
|
Cache Size | When using cursors, this is the row size of the tuple cache. If not using cursors, this is how many tuples to allocate memory for at any given time. The default is 100 rows for either case. |
|
Max LongVarChar | The maximum precision of the LongVarChar type. The default is 4094 which actually means 4095 with the null terminator. You can even specify (-4) for this size, which is the odbc SQL_NO_TOTAL value. |
|
ReadOnly | Whether the datasource will allow updates. |
|
Show System Tables | The driver will treat system tables as regular tables in SQLTables. This is good for Access so you can see system tables. |
|
LF <-> CR/LF conversion | Convert Unix style line endings to DOS style. |
|
Updatable Cursors | Enable updateable cursor emulation in the driver. Fred will be implementing real Updatable ResultSets. |
|
Row Versioning | Will turn on MVCC currency control mode, once we implement this. |
|
True is -1 | Represent TRUE as -1 for compatibility with some applications. |
|
Int8 As | Define what datatype to report int8 columns as. |
|
Extra Opts |
Extra Opts: combination of the following bits.
|
|
OID Options |
|
|
OID Options |
Level of rollback on errors: Specifies what to rollback should an error occur.
default value is a sentence unit (it is a transaction unit before 8.0). |
|
Connection Settings | The driver sends these commands to the backend upon a successful connection. It sends these settings AFTER it sends the driver "Connect Settings". Use a semi-colon (;) to separate commands. This can now handle any query, even if it returns results. The results will be thrown away however! |
The HyperSQL Engine distribution contains these same ODBC client
code examples in the sample subdirectory.
See the above section for descriptions and usage details. This section just contains a list of the available settings.
Table 17.1. Settings List
| Keyword | Abbrev. | Default Val. | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | N/A | Data source description | |
| Servername | N/A | [required] | Name of Server |
| Port | N/A | 9001 | HyperSQL Server Listen Port |
| Username | N/A | [required] | User Name |
| Password | N/A | [required] | Password |
| Debug | B2 | 0 | MyLog logging level |
| Fetch | A7 | 100 | Fetch Max Count Test to see if this applies to EXECDIRECT and/or prepared queries |
| Socket | A8 | 4096 | Socket buffer size |
| ReadOnly | A0 | No/0 | Read Only |
| CommLog | B3 | 0 | Log communications to log file |
| UniqueIndex | N/A | 1 | Recognize unique indexes |
| UnknownSizes | A9 | 0 [= max prec. for type] | Unknown result set sizes |
| CancelAsFreeStmt | C1 | 0 | Cancel as FreeStmt |
| UnknownsAsLongVarchar | B8 | 0 | Unknowns as LongVarchar |
| BoolsAsChar | B9 | 0 | Bools as Char |
| MaxVarcharSize | B0 | 255 | Max Varchar size. Value of 0 will break everything. We will be changing 0 to mean unlimited and will then change the default to 0. |
| MaxLongVarcharSize | B1 | 8190 | Max LongVarchar size |
| RowVersioning | A4 | 0 | Row Versioning |
| ShowSystemTables | A5 | 0 | Show System Tables |
| DisallowPremature | C3 | 0 | Disallow Premature |
| UpdatableCursors | C4 | 0 | Updatable Cursors |
| LFConversion | C5 | 1 Windows, 0 UNIX | LF <-> CR/LF conversion |
| TrueIsMinus1 | C6 | 0 | True is -1 |
| BI | N/A | 0 | Datatype to report BIGINT columns as |
| LowerCaseIdentifier | C9 | 0 | Lower case identifier |
| SSLmode | CA | disable | SSL mode |
| AB | N/A | Connection string suffix options |
Abbreviations are for use in connection strings.
$Revision: 6787 $